Eye Biology
Eye Biology: A Deep Dive into How We See the World
Have you ever stopped to truly appreciate the incredible complexity of your eyes? Vision is arguably our most crucial sense, yet the mechanism behind it—the entire world of Eye Biology—often remains a mystery. Understanding how your eyes capture light, convert it into electrical signals, and send those signals to your brain is nothing short of astounding.
This journey into Eye Biology will help you grasp the essential structures and processes that allow you to read these words right now. We'll explore the eye not just as an organ, but as a marvel of engineering, complete with lenses, photoreceptors, and dedicated neural pathways. Ready to see the world from the inside out? Let's begin.
The Anatomy of Sight: Key Components of the Eye
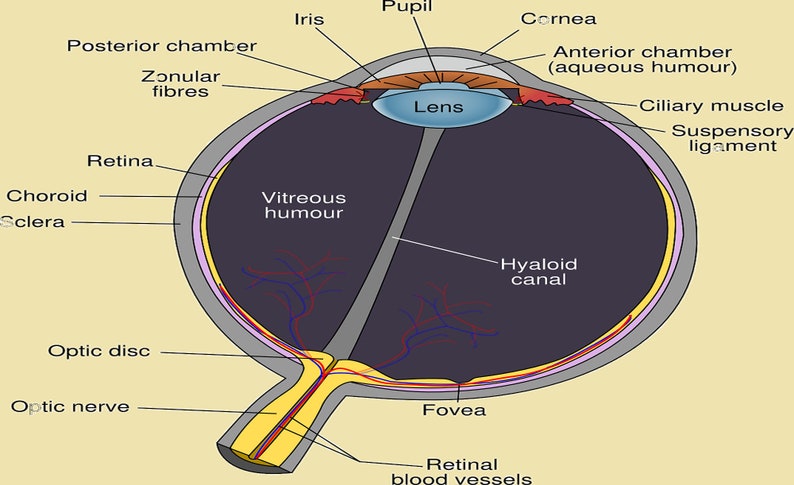
Think of the eye as a sophisticated biological camera. Just like a camera, it needs components to focus light, control aperture, and capture the final image. When we study Eye Biology, these components are grouped into the layers that protect and power our vision.
The entire structure is held within a protective socket in the skull, ensuring it remains safe from harm. But what are the crucial parts working together every second?
The Front Line: Cornea and Lens
The first interaction light has with your eye is through the cornea. This transparent, dome-shaped outer layer is responsible for bending or refracting most of the light entering the eye. It acts as the primary focusing element.
Behind the cornea, we find the iris, which controls the size of the pupil—the black opening in the center. The iris functions just like the aperture in a camera, adjusting the amount of light that reaches the inner structures. This protective mechanism is essential for adapting to various light conditions.
Next comes the lens, located just behind the iris. The lens fine-tunes the focus. Unlike the cornea, the lens is flexible; it changes shape in a process called accommodation, allowing us to focus clearly on objects both near and far. This flexibility, unfortunately, decreases with age, as we'll discuss later.
The Camera Film: Retina and Photoreceptors
Once light has been focused by the cornea and the lens, it lands on the retina, the sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye. The retina is often compared to the film or sensor chip in a camera because this is where the magic of light conversion happens.
The retina contains millions of specialized cells known as photoreceptors. These cells are the cornerstone of Eye Biology, as they are the ones sensitive to light. There are two main types of photoreceptors:
- Rods: Extremely sensitive to light intensity. Rods allow us to see in dim lighting and are responsible for black-and-white vision.
- Cones: Require much brighter light but are essential for color vision and fine detail. Cones are highly concentrated in the macula, the central part of the retina.
When light hits a photoreceptor, it triggers a complex chemical reaction. This reaction converts light energy into electrical signals, which is the language the brain understands.
How Vision Works: From Light to Brain Signal
The process of vision, from initial light absorption to final interpretation by the brain, is a lightning-fast sequence. It starts the moment you open your eyes and continues without fail until you close them again. This biological sequence is incredibly reliable.
The process involves many steps in rapid succession. Let's look at the basic flow of information:
- Light enters the eye and is refracted by the cornea.
- The pupil adjusts to regulate the light intensity.
- The lens fine-tunes the focus onto the retina.
- Photoreceptors (rods and cones) absorb the light, initiating a phototransduction cascade.
- The resulting electrical signals are processed by intermediate cells in the retina (like bipolar and ganglion cells).
- These signals converge and exit the eye via the optic nerve.
- The visual cortex in the brain receives the signals and interprets them as the image we consciously perceive.
Understanding this visual pathway is crucial to understanding the full scope of Eye Biology and why damage to any part of this system can impair sight.
The Role of the Optic Nerve
If the retina is the sensor, the optic nerve is the high-speed data cable connecting the eye to the central processing unit—the brain. This massive bundle of nerve fibers transmits all the visual information gathered by the retina.
Interestingly, where the optic nerve exits the eye, there are no photoreceptors. This spot is known as the optic disk, or more commonly, the blind spot. Our brain automatically fills in the missing information, so we never notice this gap in our visual field.
Any disease that affects the optic nerve, such as glaucoma, can severely impair the transmission of visual information, leading to permanent vision loss. Therefore, maintaining the health of this vital structure is paramount.
Common Issues in Eye Biology
Despite their robustness, eyes are susceptible to numerous conditions. Many common vision problems arise when there are structural deviations in the shape of the eye or when biological aging begins to affect the focusing elements.
We usually categorize these issues based on which part of the optical system is malfunctioning, whether it involves improper light bending or degradation of the tissues.
Refractive Errors
Refractive errors occur when the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing directly onto the retina. This is often the simplest biological issue to fix, usually requiring glasses, contacts, or minor surgical correction.
The most common refractive errors include:
- Myopia (Nearsightedness): The eyeball is slightly too long, or the cornea is too steeply curved, causing light to focus in front of the retina. Distant objects look blurry.
- Hyperopia (Farsightedness): The eyeball is too short, or the cornea is too flat, causing light to focus theoretically behind the retina. Near objects appear blurry.
- Astigmatism: The cornea or lens has an irregular curvature (more like a football than a baseball), causing blurred vision at any distance.
Age-Related Changes
As we age, biological processes naturally lead to changes in eye function. These changes are universal and demonstrate the impact of time on the lens and other vital structures.
Presbyopia, often noticeable after age 40, is one such condition. This happens because the lens loses its flexibility and can no longer change shape easily to focus on close objects, requiring reading glasses.
Another prevalent age-related issue is cataracts, where the normally clear lens becomes cloudy. This clouding scatters light and reduces vision clarity, requiring surgical replacement of the lens to restore sight. These biological changes highlight the fragility of our visual system over the lifespan.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Marvelous Eyes
Eye Biology is a fascinating field, revealing how complex structures—from the clear cornea to the delicate, light-sensitive retina—work in perfect synchrony to deliver vision. The ability to capture light and translate it into a perceived image in real-time is an achievement that few biological systems can match.
Whether you wear glasses or have perfect 20/20 vision, remember the incredible biological machinery at work. Protect your eyes by wearing sunglasses outdoors, maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins like A and C, and never skipping your routine eye exams. Cherish your vision; it truly is a gift built upon millions of years of biological evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Eye Biology
- What is the difference between the cornea and the lens?
- The cornea is the outermost transparent layer responsible for the majority of light refraction. The lens sits behind the iris and fine-tunes the focus (accommodation) for objects at different distances.
- Why do we have a blind spot, according to Eye Biology?
- The blind spot (optic disk) exists because it is the point where the ganglion cell axons gather to form the optic nerve and exit the eyeball. Since there are no photoreceptors (rods or cones) in this specific area, no visual information can be gathered there.
- Can diet affect Eye Biology?
- Absolutely. Many nutrients are vital for eye health. Antioxidants found in leafy greens (like Lutein and Zeaxanthin) protect the macula, while Vitamin A is essential for the function of rods, helping with night vision.
- How does the brain interpret the upside-down image projected onto the retina?
- The lens projects an inverted and reversed image onto the retina. The brain's visual cortex is trained from birth to interpret this inverted input as upright. It processes the information and flips the perceived image in the final stage of vision.
Eye Biology
Eye Biology Wallpapers
Collection of eye biology wallpapers for your desktop and mobile devices.

Vibrant Eye Biology Capture for Mobile
Explore this high-quality eye biology image, perfect for enhancing your desktop or mobile wallpaper.
Crisp Eye Biology Background in HD
A captivating eye biology scene that brings tranquility and beauty to any device.
Exquisite Eye Biology Landscape Concept
This gorgeous eye biology photo offers a breathtaking view, making it a perfect choice for your next wallpaper.

Exquisite Eye Biology View for Mobile
A captivating eye biology scene that brings tranquility and beauty to any device.
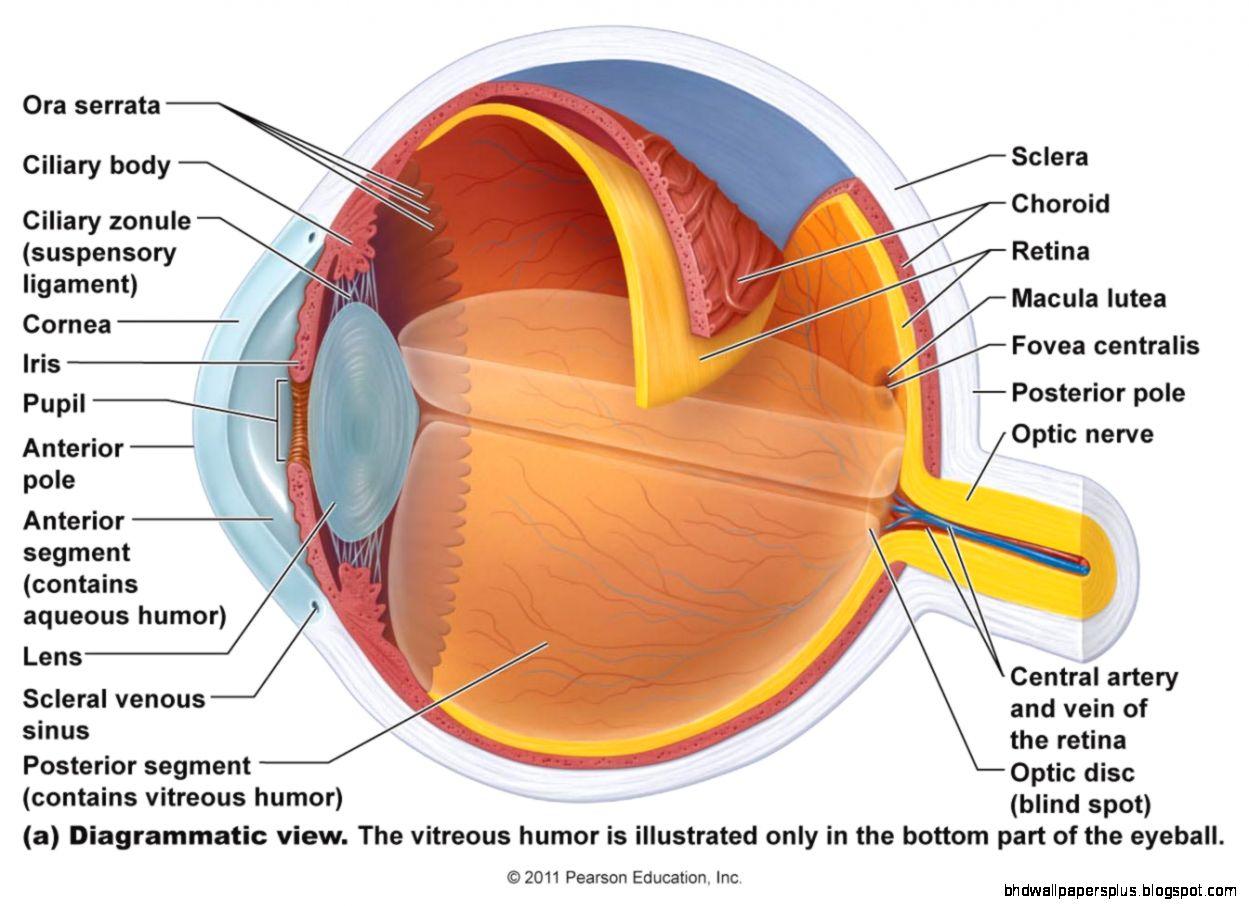
Beautiful Eye Biology Artwork for Mobile
Transform your screen with this vivid eye biology artwork, a true masterpiece of digital design.

Crisp Eye Biology Scene Photography
This gorgeous eye biology photo offers a breathtaking view, making it a perfect choice for your next wallpaper.

Detailed Eye Biology Design for Desktop
Transform your screen with this vivid eye biology artwork, a true masterpiece of digital design.

Stunning Eye Biology Design for Desktop
A captivating eye biology scene that brings tranquility and beauty to any device.
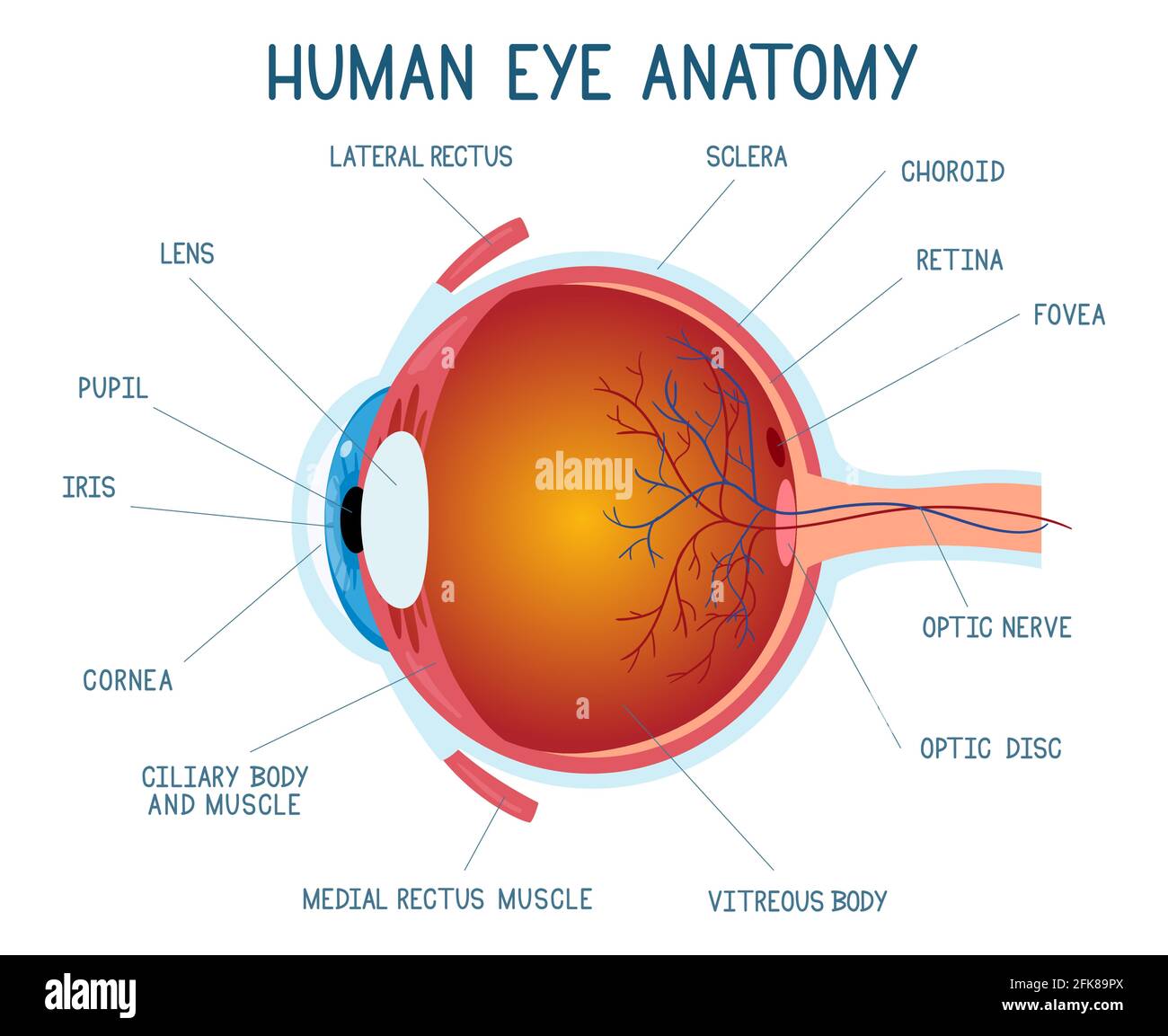
Vibrant Eye Biology View for Mobile
Discover an amazing eye biology background image, ideal for personalizing your devices with vibrant colors and intricate designs.

Stunning Eye Biology Landscape Concept
Immerse yourself in the stunning details of this beautiful eye biology wallpaper, designed for a captivating visual experience.

Breathtaking Eye Biology Landscape in 4K
Explore this high-quality eye biology image, perfect for enhancing your desktop or mobile wallpaper.

Captivating Eye Biology Picture Digital Art
Find inspiration with this unique eye biology illustration, crafted to provide a fresh look for your background.

Gorgeous Eye Biology Image Art
Immerse yourself in the stunning details of this beautiful eye biology wallpaper, designed for a captivating visual experience.

Serene Eye Biology Landscape Digital Art
Experience the crisp clarity of this stunning eye biology image, available in high resolution for all your screens.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg)
Dynamic Eye Biology Design for Desktop
Find inspiration with this unique eye biology illustration, crafted to provide a fresh look for your background.

Vibrant Eye Biology Design Illustration
Discover an amazing eye biology background image, ideal for personalizing your devices with vibrant colors and intricate designs.

Beautiful Eye Biology Capture Concept
Explore this high-quality eye biology image, perfect for enhancing your desktop or mobile wallpaper.
Serene Eye Biology Design Illustration
Discover an amazing eye biology background image, ideal for personalizing your devices with vibrant colors and intricate designs.

Breathtaking Eye Biology Landscape Photography
Experience the crisp clarity of this stunning eye biology image, available in high resolution for all your screens.

Gorgeous Eye Biology Wallpaper Illustration
A captivating eye biology scene that brings tranquility and beauty to any device.
Download these eye biology wallpapers for free and use them on your desktop or mobile devices.